We can easily assume that the nearest we come to the Sun would be the hottest when we talk of planets. The sunshine reaches it the most, does it? But space is not necessarily common sense. And, when you have ever questioned yourself about which is the hottest planet in solar system, it is not Mercury, but actually Venus.
The second planet Venus is the hottest recorded planet though it is closer to our Sun compared to Mercury. It is an unbelievable example of atmospheric science that can violate the rule. Here, the article will talk about why Venus is hotter than Mercury, the reason for Venus to get so hot, and what it can teach us about the climate of the planet, Earth.
What Is the Hottest Planet in the Solar System?
The issue of the question of the hottest planet in the solar system might not appear that difficult but the answer to this question is interesting physics and planetary science. Venus is the hottest planet since the surface temperature is about 464 o C. That’s hot enough to melt lead. The nearest one to the Sun is mercury which should be hotter. But there is no important atmosphere in Mercury, and the heat is easily lost there.
The atmosphere in Venus on the other hand is rich in carbon dioxide (CO 2) that is a good trapper of heat. This wrapping of nature is what is causing Venus to be an oven of a planet and it is burning by day and night.
| Planet | Distance from Sun (km) | Average Temperature (°C) | Atmosphere Composition |
| Mercury | 58 million | 167 (max 430, min -180) | Thin exosphere |
| Venus | 108 million | 464 | 96% carbon dioxide |
| Earth | 150 million | 15 | 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen |
Why Is Venus the Hottest Planet Despite Being Farther from the Sun?
It appears that it is impossible that Venus is hotter than Mercury in the first place. Mercury is very close to the Sun hence having more sunshine but the heat does not stay due to the absence of the dense atmosphere. During the evening, on Mercury, the temperature is -180 o C. In contrast to that, Venus does not lose its heat as a result of its runaway greenhouse effect. The CO 2 blanket catches the sunlight in its dense atmosphere and sends the reflections back to the infrared radiation.
Therefore, Venus is never cold regardless of whether it is facing the Sun or not. The temperature is further worsened by the fact that the surface pressure of Venus is about 90 times higher than that of the earth. Here is Venus (or death), to think of living in such a thick atmosphere as that, to squeeze the metal in a few minutes.
| Factor | Venus | Mercury |
| Distance from Sun | 108 million km | 58 million km |
| Average Temperature | 464°C | 167°C |
| Atmosphere | Dense CO₂ | Almost none |
| Night Temperature | 462°C | -180°C |
How Does the Greenhouse Effect Make Venus So Hot?
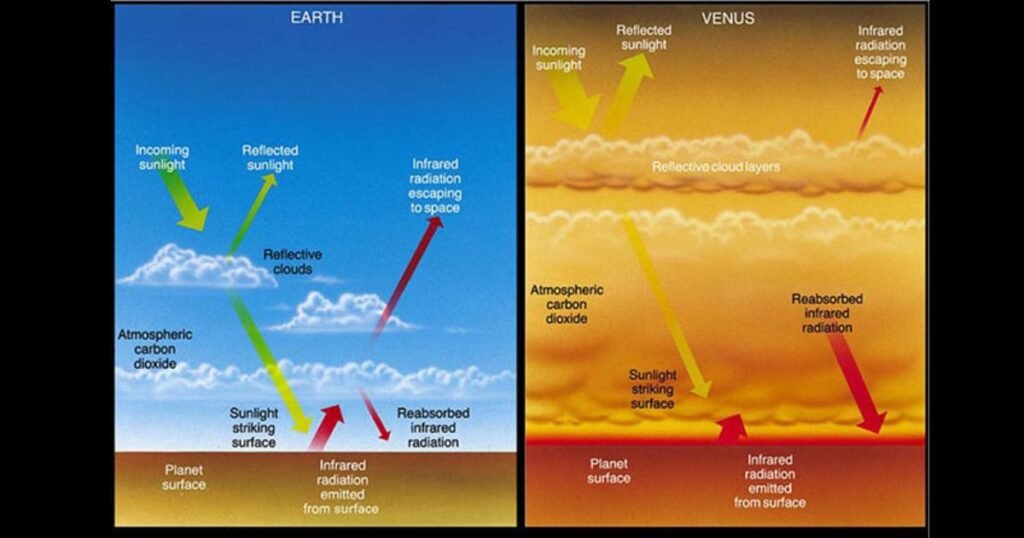
Green house effect is a phenomenon that happens when the sunlight heat is absorbed by gases accumulated in the air of a planet. This radical process happens on Venus. Infrared radiation is re-emitted as a result of solar irradiation reflected on the surface of the planet. This heat is not lost in space but is reabsorbed by carbon dioxide molecules. It ultimately creates a heat trap of its own in the long run, a runaway greenhouse effect.
This is because this effect maintains almost similar temperatures in the entire planet. It burns at about 464 o C, either day or night, at equator or pole, Venus burns.
Key points about Venus’s greenhouse effect:
- The atmosphere is 96% carbon dioxide.
- Clouds contain sulfuric acid, reflecting sunlight yet trapping heat.
- Surface pressure is 92 times Earth’s.
- No temperature difference between day and night.
This same phenomenon keeps Earth habitable, but on Venus, it went out of control.
What Is Mercury’s Role in Comparison?
To have full appreciation of the fact that Mercury is not the hottest planet in the solar system we need to be aware of the reasons why it is not the hottest planet. The closest one is Mercury that rotates at just 58 million kilometers. It is also not receiving any photo-reality atmosphere. Mercury has a layer of particles which takes the place of the atmosphere of a planet.
These are the micrometeorite and solar atoms that are not sufficient to trap heat. This leads to drastic shifts in the temperatures of Mercury to 430 C in the day and -180 C in the night. Mercury is hence a place of extremes so to speak, in that it overheats during the day and will freeze at night, and vice versa, Venus is an inferno.
What is the Comparison between Venus and Earth and Mercury?
Although Venus is usually regarded as being a twin Planet to Earth, due to the fact that it is also large and dense, the similarities end here. We shall compare them to each other to make the differences more distinct.
| Feature | Venus | Earth | Mercury |
| Size | Slightly smaller than Earth | — | Smaller |
| Average Temp | 464°C | 15°C | 167°C |
| Atmosphere | CO₂ + Sulfuric Acid Clouds | Nitrogen + Oxygen | Thin exosphere |
| Pressure | 92 bars | 1 bar | 0 |
| Rotation | Retrograde (243 Earth days) | Normal (24 hours) | 59 Earth days |
Based on this table, one can observe that the conditions on Venus are radically different. It has a long rotation period, thick air and an atmosphere of CO 2 and all this makes it an extreme and unlivable environment.
What Happened to Venus’s Water?
Scientists are sure that the oceans may have existed on Venus. It may have been similar to the one we are presently living in warm, wet and could have been habitable billions of years ago. The sunshine did not evaporate water gradually, however. The water vapor, which is, in its turn, a greenhouse gas, entered the atmosphere in the cases that caused the planet to get even warmer. This augmented the degree of evaporation due to the high temperature and this started a vicious cycle where all the water was evaporated in Venus.
Any hydrogen that did not evaporate in the form of water would have probably been lost to space today. This change renders Venus a caution on what may occur when the greenhouse gases go astray.
What Does Venus Teach Us About Climate Change?
The story of which is the hottest planet in solar system holds a deep environmental message. Venus serves as a practical example of what can take place when greenhouse gases take over the atmosphere of a planet.
On this planet, the quantity of CO 2 in the atmosphere is approximately 0.04 percent and this keeps the temperature constant. On Venus, that number is 96%. That difference in itself made a once potentially habitable world a furnace.
The comparison is crucial to climate studies in the modern world. Venus demonstrates the possible extreme course of the direction of the carbon levels on the Earth should they grow without any control.
Key lessons from Venus:
- Greenhouse gases can radically alter a planet.
- Once a runaway effect starts, it’s irreversible.
- Atmospheric balance is key to maintaining habitability.
Can We Ever Visit Venus?
The surface conditions of Venus make the planet almost impossibly accessible to man. The strain would tear apart the frying of the electronics of a spacecraft. Nonetheless, researchers are considering how to research Venus as a planetary atmosphere. Floating stations have been suggested by other people and they will be floating in the upper part of the planet which is colder at 30 o C and the breathing of the pressure is possible. The so-called cloud cities, this time, may enable us to view Venus in the future, safely, and unveil its secrets.
Example:
The Soviet Venera 13 landed on the Venus surface in 1982, and survived only 127 minutes under pressure and heat.
What Are Some Interesting Facts About Venus?
Venus is an interesting planet, full of contradictions and surprises. The following are some of the facts that render it unique:
- Venus takes a year of 243 days longer than a day on Venus.
- It revolves in the opposite way, that is, the Sun sets in the west.
- It is so dense in atmosphere that sound travels more rapidly.
- The surface pressure is the same pressure where one is 900 meters deep in the ocean.
- It is the hottest planet though the brightest object in the sky at night since it reflects 75 percent of the sun rays.
It is all facts that demonstrate why Venus is an extreme planet, scorching and deadly.
How Does Venus Inspire Space Missions?
Several missions have already made studies of Venus itself and more are yet to be seen. NASA VERITAS mission and ESA EnVision mission are meant to investigate the surface and atmosphere of Venus. Such missions will research the volcanic activity, surface changes and chemical composition of the planet. They can even help to provide the answer to the question of how Venus became a potential water world into a barren wasteland. The atmosphere of the earth is better comprehended through the study of Venus. The responses would help in curbing the climatic disasters in this country.
Conclusion: Which is the hottest planet in solar system?
The clear answer is Venus. It is not closest to the Sun but it is warmer than any others because of its dense atmosphere of carbon dioxide. Its surface reaches about 464 C, hence hotter than Mercury, the Earth or any other planet. Venus is an incendiary product of what can become wrong with the greenhouse effect. It is in fact a mystery and danger, an indication both of beauty and destruction. In our continued exploration of the universe, Venus will never cease to be a representation of what could happen in the event that the fine balance of the planet Earth is ever destabilized.
Also Read About: Who Discovered Solar System: The Story Behind Our Cosmic
